|
| 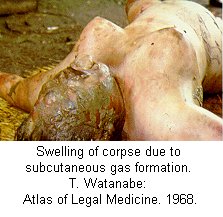 | |||
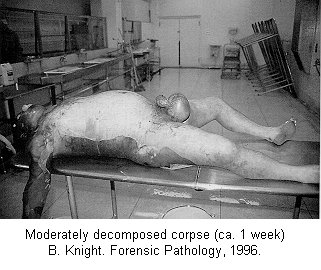
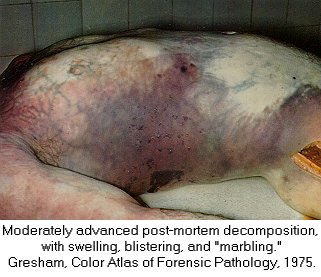
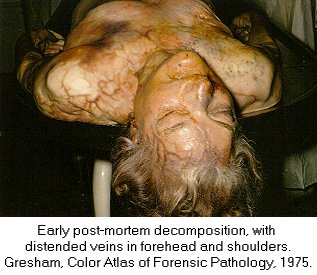
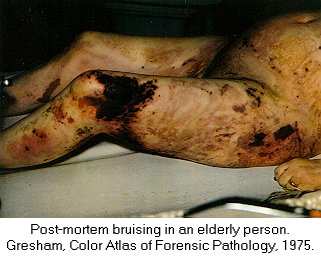
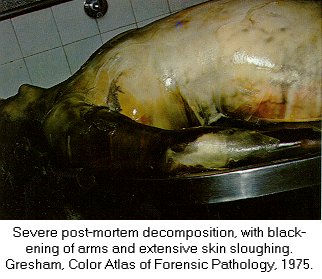
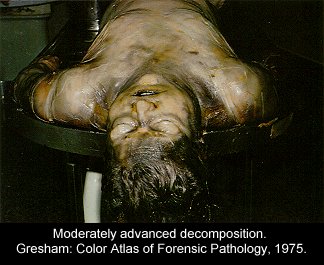
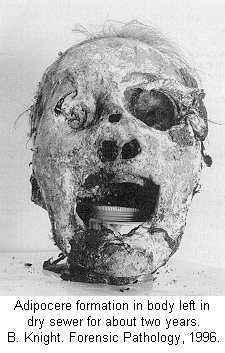
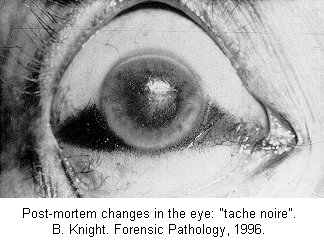
| Forensic Pathologist examine the remains of a body by doing and autopsy. They do this in an attempt to determine time and cause of death. This field involves the investigation of sudden, unnatural, unexplained, or violent deaths. The primary role of the Forensic Pathologist is to determine cause of death either through observation or by autopsy. There are five categories that can classify the manner in which death occurred: natural, homicide, suicide, accident, or undetermined, based on the circumstances surrounding the incident. For the Forensic Pathologist there are four basic type of wounds they look for: Puncture (stab, bullet, shotgun), Abrasion (blow, bludgeon, sliding), Incision (slash, slice), and Laceration (tear, jagged glass). In determining time of death Forensic Pathologist look at what we call rate methods and concurrent methods. Rate Methods Rigor Mortis The first rate method is Rigor Mortis. This is called the stiffening of death because immediately after death the muscles relax and then become rigid without the shortening of the muscle. It's Onset is Immediate. Detected 2-4 hours after death. Complete 6-12 hours after death. Remains 12-18 hours after death. Leaves in 24-36 hours after death. Completely gone in 40-60 hours after death. There are a number of things that can affect rigor mortis such as; strenuous muscular activity, enviornmental temperatures (hotter faster it sets) (colder slower it sets), and body temperature at the time of death. This is an unreliable technique for determining time of death. Livor Mortis (Lividity) Called the pulling of the blood because the heart stops pumping and the blood begins to settle in the parts of the body closest to the ground. The skin will become dark blue or purple in these areas. The onset is immediate, visible 1/2-4 hours after death, well developed 3-4 hours after death, maximum 8-12 hours after death, and it never disappears. A number of things can also affect Livor Mortis including; acute blood loss or anemia prior to death makes this less visible and Carbon Monoxide or Syanide poisoning turn the skin this color any way. This is a bad technique for determining time of death. Algor Mortis This is the cooling after death. Your body temperature continually cools 1.5 degrees each hour until it reaches room temperature. The body temperature will not get any cooler than room temperature. This is influenced by size of the victim, clothing, weather conditions, and location of the body. Decomposition Stage where the body begins to rot through seven different methods. 1.) Blue-Green Discoloration: the skin, beginning in the abdomen, goes from left to right quadrant of the abdomen and then to the whole stomach region. 24 hours after death left and right quadrant are blue-green, 36 hours after death the whole stomach is blue-green, 36-48 bloating sets in. 2.) Bloating: the loose skin areas on the body start to swell. 3.) Marbling: starts 2-3 days after bloating. There is a chemical reaction in the blood that causes a green black discoloration of the veins. 4.) Skin Slippage: Occurs 7 to 4 days after death. The skin literaly slides off the body. 5.) Adipocere: This takes months, and only occurs when the body is continually in the presence of moisture. It forms a waxy residue onto the skin. 6.) Mummification: Takes months, sometimes years. Happens when body moisture is less than 50%. 7.) Skelitanization: When the flesh is no longer a part of the body. Takes weeks or years. Enviornmental factors affect decomposition such as; temperature, insects, cause of death. Flora This is the plant life that can be found around the body and grass around and beneath the body. This is determined by a Forensic Botanist. Fauna This is insects, which are best for determining minimal post mortem intervals. Insects that can usually be found on the body after death. Body Lice, Blow Flies, and Beetles. Body Lice will remain on the host anywhere from 3 to 6 hours after death. Blow Flies will find the body with in ten minutes after death. They will immediately lay eggs, then hatch in 18 to 24 hours after death. Beetles feed off the dry skin and other insects that come. Concurrent Methods Concurrent methods look at the factors outside of death to determine time of death such as a broken watch. Corporal Evidence Evidence that is in the body, such as food in the stomach and occular changes. Ten minutes after you eat your food starts to go away. Light Meal 1-11/2 to go away, medium meal 3-4 hours to go away, heavy meal 4-6 hours to go away. Occular changes depend entirely on whether or not the eyes were opened or close at the time of death. 1st occular change, film appears on the eye, if opened takes minutes, if closed takes hours. 2nd occular change, the eyes begin to get cloudy, if open 2 hours, if closed 24 hours. 3rd occular change, the eyes begin to bulge. This is a result of decomposition. Identifying The Unknown When trying to identify the unknown the best method to use is fingerprints. You can try to determine their occupational trademark by looking at their hands, you can examine their clothing for clues, look into missing persons, internal examination and the last least preferred method is family identification.
|
| |||
|
Click thumbnail above to see body in the early Blue-Green Decomposition phase Click on the the thumbnail above to see a corpse in the Marbling Stage of Decomposition
Click the thumbnail above to see another Marbling corpse Click on the thumbnail above to see a corpse in the Livor Mortis Stage Click on the thumbnail above to see a picture of a corpse in the Skin Sloughing stage of Decomposition Click on the thumbnail above to see a corpse in what I think is Adipocere stage of Decomposition
Click on the thumbnail above to see a corpse with Mummification | ||||
 | ||||
Return to Main Page |